For the first time, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has released an e-book version of its Guide to Clinical Preventive Services. The e-book is compatible with many readers, including Kindle, Nook, iBook, and Kobo. The new “Guide to Clinical Preventive Services, 2014” is a comprehensive resource that can help primary care clinicians and patients decide together which preventive services are right for a patient’s needs. It includes all active Task Force evidence-based recommendations since 2004, including 28 new and updated recommendations since the 2012 guide, in a format meant for use at the point of patient care. It also includes information about topics in development, clinical summary tables and additional resources.
copy deeplink MCN's Technical Comments for the Worker Protection Standard
MCN's Technical Comments for the Worker Protection StandardOn Monday August 18, 2014 MCN submitted technical comments to the EPA regarding the proposed changes to the Worker Protection Standard. View MCN's recommendations for advancing stronger safeguards to protect farmworkers from pesticide exposure.
- MCN_WPS_FinalComments_2014.pdf (164.74 KB)
copy deeplink Policy Memo on Farm Worker Housing in Skagit Valley
Policy Memo on Farm Worker Housing in Skagit ValleyThis proposal will I) provide a profile of the agricultural industry and Farmworkers in Washington State II) propose a theoretical framework to understand farmworker housing accessibility III) describe prior legislative actions to address farmworker housing IV) and propose a set of recommendations to address farmworker housing.
copy deeplink The Year in US Occupational Health & Safety
The Year in US Occupational Health & SafetyThis report captures important happenings in occupational health and safety from August 2013 through July 2014. Authoured by researchers from the George Washington University Milken Institute School Of Public Health, this resource focuses on workplace injury and illness statistics each spring and documents successes, challenges, and areas ripe for improvement in occupational health and safety.
copy deeplink MCN's Position on Children Crossing the Border
MCN's Position on Children Crossing the BorderPublished July 15, 2014
MCN holds the position that immigrant children fleeing violence in their home countries must receive priority consideration for their safety and health. We have provided several links with additional resources on this issue.
http://umash.umn.edu/needlestick-prevention/ This webpage features factsheets and videos developed by the Upper Midwest Agricultural Safety and Health Center (UMASH) to educate farmworkers, producers, and veterinarians about needlestick prevention. Resources are available in both English and Spanish.
copy deeplink Press Release: Work. Respect. Dignity. Shared Images and Stories of Maryland's Eastern Shore Immigrants
Press Release: Work. Respect. Dignity. Shared Images and Stories of Maryland's Eastern Shore ImmigrantsA photo exhibit at Salisbury University’s Downtown Art Gallery depicts the lives, work, and stories of immigrants on Maryland’s Eastern Shore. An exhibit reception and panel discussion on September 18 will include an immigrant who is featured in the images and experts in photojournalism, cultural studies, immigration and migrant health.
- PressRelease_Final_09.09.14.pdf (205.8 KB)
copy deeplink Seguridad en palabras – Diccionario ilustrado bilingüe para la agricultura | COMIC
Seguridad en palabras – Diccionario ilustrado bilingüe para la agricultura | COMICEste diccionario ilustrado bilingüe de MCN, "Seguridad en Palabras/ Safety in Words", muestra los peligros que hay en el lugar de trabajo y las mejores prácticas para la salud y la seguridad en la agricultura. Desarrollado con el apoyo del Programa de Subvenciones Susan Harwood de OSHA, este recurso refuerza el vocabulario en inglés de los trabajadores que hablan español lo que ayudará a prevenir lesiones en la agricultura.
View a brief overview of who MCN is and how we work to create practical solutions at the intersection of poverty, migration, & health.
copy deeplink 2013 A Year In Review | Migrant Clinicians Network
2013 A Year In Review | Migrant Clinicians NetworkTake a look at the highlights of MCN's services and programs in action during 2013!
Other versions:
View Large
Download PDF
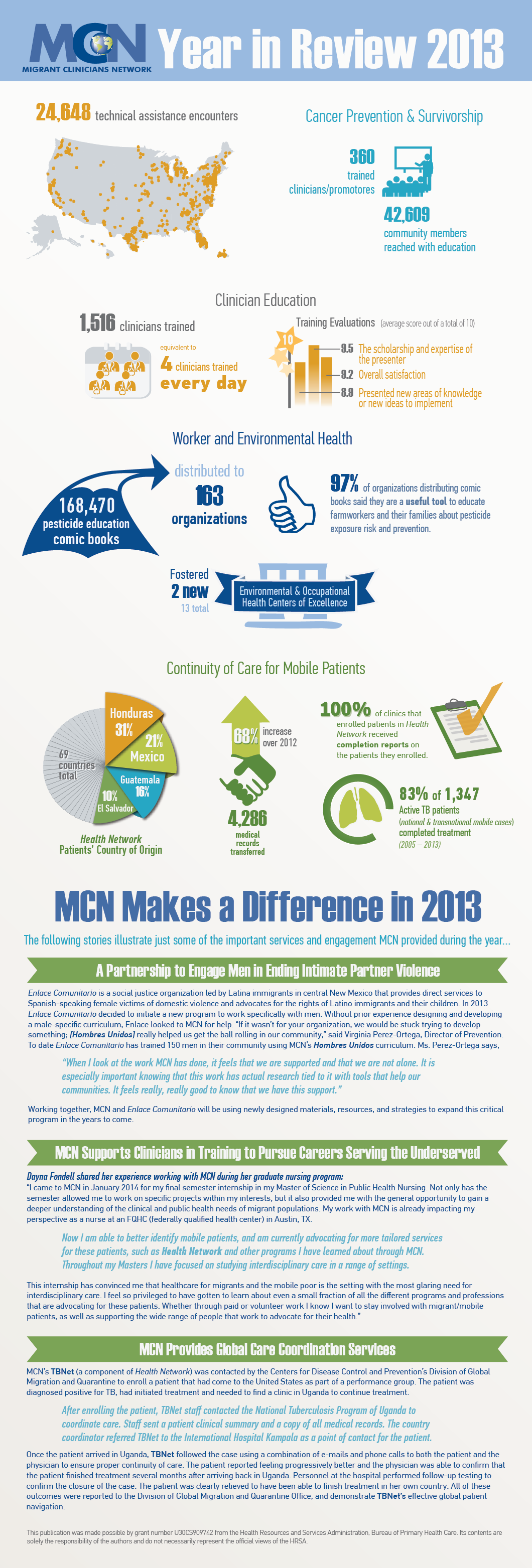
- YiR_for office printer (no bleed)_0.pdf (1.59 MB)
copy deeplink Theater in the Fields: A Guide for Dynamic Outreach with Farmworkers
Theater in the Fields: A Guide for Dynamic Outreach with FarmworkersNew bilingual resource available April 2014!
Student Action with Farmworkers (SAF) has been using theater as an educational tool with farmworkers for over twenty years. By drawing on techniques of popular theater, SAF performs culturally appropriate, lively skits and facilitates theater workshops at farm labor camps. These performances spur conversations about mental and physical health, living and working conditions, and farmworker movements for social justice.
Many of SAF’s performances have focused on health issues, and they aim for this guide to offer dynamic tools for health care providers, educators, outreach workers, and public health innovators. Practitioners can also use these techniques with other populations across the social justice spectrum. For both organizers and educators, SAF hopes that popular theater can bolster the messages and information that you so readily share and provide a dynamic approach to outreach. Resources include songs, scripts, theater games and icebreakers. Printed copies are free, but SAF accepts small contributions to cover shipping and handling ($5-10/copy).
Available in print and online
Contact: Laxmi Haynes , 919-660-3660
1. New Tobacco Measure: (combining two previous measures)
MEASURE: Patients age 18 and older (1) screened for tobacco use AND (2) received cessation counseling intervention or medication if identified as a tobacco user one or more times in the measurement year or prior year
2. New HIV cases with timely follow-up:
MEASURE: Patients whose first ever HIV diagnosis was made by health center staff between October 1 and September 30 and who were seen for follow up within 90 days of that first ever diagnosis
3. PATIENTS SCREENED FOR DEPRESSION AND FOLLOWED UP AS APPROPRIATE
MEASURE: Patients aged 12 and over who were (1) screened for depression with a standardized tool and (2) had a follow-up plan documented if patients were considered depressed
copy deeplink Approved Uniform Data System Changes for Calendar Year 2014
Approved Uniform Data System Changes for Calendar Year 2014Program Assistance Letter
- UDS_2014_Changes.pdf (712.39 KB)
These files are part of the Engaging Migrant Men project.
MCN developed 3 vignettes that portray the three messages developed in video and printed form.
- palabras_BI.pdf (354.68 KB)
- Palabras_SP.pdf (354.01 KB)
- para_BI.pdf (282.97 KB)
- para_SP.pdf (335.13 KB)
- vio 3 topics booklet_BI.pdf (371.19 KB)
- vio 3 topics booklet_SP.pdf (364.91 KB)
- violencia_BI as flyers.pdf (578.78 KB)
- violencia_SP as flyers.pdf (569.02 KB)
copy deeplink Engaging Migrant Men Discussion Guide Informational Packet
Engaging Migrant Men Discussion Guide Informational PacketThese files are part of the Engaging Migrant Men project.
Accompanying discussion guides were created to be used by male peers, community leaders, or outreach workers for one-on-one and small group discussions with men.
National Center for Infectious Diseases, Division of Parasitic Diseases - Provides overview of numerous water-borne and sanitation related diseases.
copy deeplink Repeated Pesticide Exposure among North Carolina Migrant and Seasonal Farmworkers
Repeated Pesticide Exposure among North Carolina Migrant and Seasonal FarmworkersLimited data document the multiple and repeated pesticide absorption experienced by farmworkers in an agricultural season or their risk factors.
copy deeplink Chronic Agricultural Chemical Exposure Among Migrant and Seasonal Farmworkers
Chronic Agricultural Chemical Exposure Among Migrant and Seasonal FarmworkersLaboratory studies and case reports of accidental exposure to large amounts of chemicals indicate that there are immediate and long‐term negative health consequences of exposure to agricultural chemicals.
copy deeplink Acute Pesticide- Related Illness Among Working Youths, 1988-1999
Acute Pesticide- Related Illness Among Working Youths, 1988-1999The goal of this study was to describe acute occupational pesticide-related illnesses among youths and to provide prevention recommendations. Survey data from 8 states and from poison control center data were analyzed.
copy deeplink Acute Occupational Pesticide- Related Illness in the US 1998-1999: Surveillance Findings From the SENSOR-Pesticides Program
Acute Occupational Pesticide- Related Illness in the US 1998-1999: Surveillance Findings From the SENSOR-Pesticides ProgramConcern about the adverse public health and environmental effects of pesticide use is persistent. Recognizing the importance of surveillance for acute occupational pesticide-related illness, we report on surveillance for this condition across multiple states. Between 1998 and 1999, a total of 1,009 individuals with acute occupational pesticide-related illness were identified by states participating in the SENSOR-pesticides program.
copy deeplink The Surveillance of Work- Related Pesticide Illness: An Application of the Sentinel Event Notification Systems for Occupational Risks( SENSOR)
The Surveillance of Work- Related Pesticide Illness: An Application of the Sentinel Event Notification Systems for Occupational Risks( SENSOR)In response to limitations in state-based occupational disease surveillance, the California Department of Health Services developed a model for surveillance of acute, work-related pesticide illness. The objectives were to enhance case reporting and link case reports to preventive interventions. Risk factors for pesticide illness were prevalent.
copy deeplink California Surveillance for Pesticide- Related Illness and Injury: Coverage, Bias and Limitations
California Surveillance for Pesticide- Related Illness and Injury: Coverage, Bias and LimitationsThe California Pesticide Illness Surveillance Program (PISP) is a major resource for pesticide illness epidemiology. This work attempts to improve characterization of pesticide illness in California, evaluate case ascertainment of the PISP and identify PISP’s limitations and biases for studying the incidence and epidemiology of pesticide-related illness.
copy deeplink Surveillance for Pesticide- Related Disease
Surveillance for Pesticide- Related DiseasePublic health surveillance for acute pesticide intoxications is discussed. Explanation of the goals, components and functions of population-based surveillance is provided with reference to key informational sources.
copy deeplink Greater Risks, Fewer Rights: U.S Farmworkers and Pesticides
Greater Risks, Fewer Rights: U.S Farmworkers and PesticidesPesticide Action Network, United Farmworkers of America, and California Rural Legal Assistance Foundation analyzed California government data on agricultural poisonings and enforcement of worker safety standards. Nearly 500 pesticide poisonings were reported for California farmworkers every year. The actual number of pesticide-related illnesses is unknown, since many poisonings go unreported.
copy deeplink Pesticide- related illness among migrant Farm Workers in the United States
Pesticide- related illness among migrant Farm Workers in the United StatesSurveillance data show that pesticide-related illness is an important cause of acute morbidity among migrant farm workers in California. Exposures occur in various ways (e.g., residues, drift), suggesting that the use of pesticides creates a hazardous work environment for all farm workers Improved education for health care providers should be a priority. Growers should be educated about alternative forms of pest control and incentives should be provided to encourage their use.
copy deeplink Development of a Surveillance Program for Occupational Pesticide Poisoning: Lessons Learned and Future Directions
Development of a Surveillance Program for Occupational Pesticide Poisoning: Lessons Learned and Future DirectionsDescribes the growth from 1987 through 1996 of the Occupational Pesticide Poisoning Surveillance Program at the Texas Department of Health. The program was initially based on a Sentinel Event Notification System for Occupational Risks (SENSOR) model, using sentinel providers to report cases, supplementing the passive reporting by physicians that was required by law.
copy deeplink Development of a Surveillance Program for Occupational Pesticide Poisoning: Lessons Learned and Future Directions
Development of a Surveillance Program for Occupational Pesticide Poisoning: Lessons Learned and Future DirectionsThe authors describe the growth of the Occupational Pesticide Poisoning Surveillance Program at the Texas Department of Health. The program was based on a Sentinel Event Notification System for Occupational Risks(SENSOR) model, using sentinel providers to report cases. The number of confirmed occupational cases increased from 9 workers in 1987 to 99 workers in 1996.
copy deeplink The Use of Audience Response System Technology With Limited-English-Proficiency, Low-Literacy, and Vulnerable Populations
The Use of Audience Response System Technology With Limited-English-Proficiency, Low-Literacy, and Vulnerable PopulationsMatthew C. Keifer, MD, MPH; Iris Reyes, MPH; Amy K. Liebman, MA, MPA; Patricia Juarez-Carrillo, PhD, MPH. Abstract. Audience response systems (ARS) have long been used to improve the interactivity of educational activities. Most studies of ARS have addressed education of literate trainees. How well these devices work with low-literacy subjects is not well studied. Information gathering on the training audience is an important use of ARS and helpful in improving the targeting of training information. However, obtaining demographic information from vulnerable populations with reasons to be concerned about divulging information about themselves has not been tested. In addition, a culturally competent method to effectively collect demographic and evaluation data of this growing population is essential. This project investigated the use of ARS to gather information from Hispanic immigrant workers, many of whom are socially vulnerable and have limited English proficiency (LEP) and low-literacy. Workers attended focus groups and were asked to use ARS devices or clickers to respond to questions. Questions were both catergorical (multiple choice) and open-ended numerical (text entry), and varied from simple queries to more sensitive points regarding immigration. Most workers answered the one-key response categorical questions with little difficulty. In contrast, some participants struggled when responding to numerical questions, especially when the response required pressing multiple clicker keys. An overwhelming majority of participants reported that the clickers were comfortable and easy to use despite the challenges presented by the more complex responses. The error rate increased as question complexity increased and the trend across three ordered categories of response complexity reached statistical significance. Results suggest that ARS is a viable method for gathering dichotomous or higher-order categorical information from LEP and low-literacy populations in a group setting while assuring anonymity. However, it is recommended that clickers be developed and tested with fewer, bigger, and more widely separated buttons, and less printing on the buttons for these populations. Further research is needed to determine the effectiveness of using clickers with simplified configurations in the workplace as a tool to collect data for surveys and assessments and to better engage LEP and low-literacy workers in training sessions.
- Keifer_etal_ARS_JAM_2014.pdf (334.48 KB)